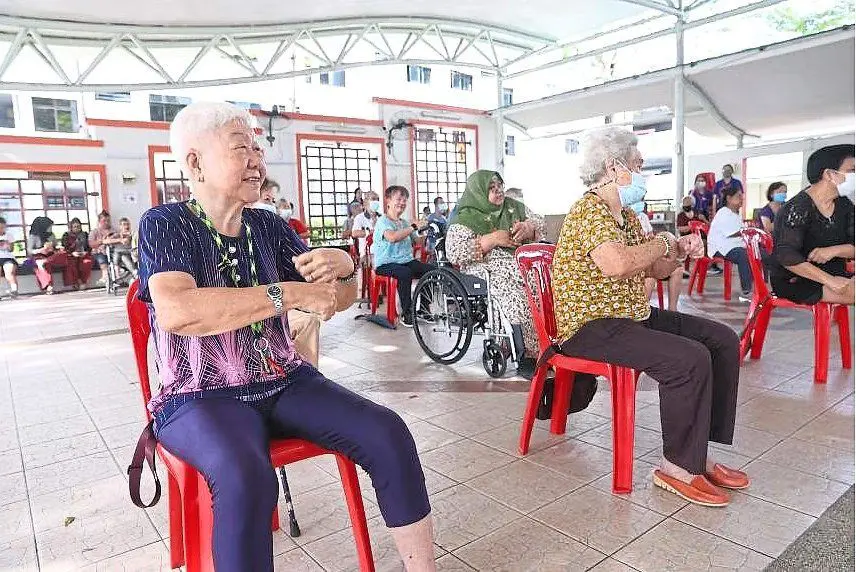
For those with limited mobility, chair exercises are a good way to work out. — The Straits Times/ANN
As individuals age, it becomes increasingly important to maintain physical activity for overall health and well-being.
Regular exercise aids seniors in managing weight, elevating mood, improving balance and lowering the risk of chronic illnesses.
However, many older adults encounter obstacles that complicate traditional forms of exercise like walking or jogging.
Mobility limitations, joint discomfort and various health issues can hinder participation in more intensive workouts, resulting in a sedentary lifestyle that may adversely affect health.
For those who find walking challenging, chair exercises offer an excellent alternative.
These low-impact movements can be performed while seated, making them both accessible and safe for seniors across all fitness levels.
Chair exercises not only encourage physical activity, but also provide numerous advantages, including enhanced cardiovascular health and improved muscle strength.
By integrating these exercises into their daily routines, seniors can improve their quality of life and maintain their independence.
Exercises for heart health
As people age, it is essential to prioritise heart health.
Below are a few effective chair exercises designed to enhance cardiovascular fitness:
Sit upright in a sturdy chair with your feet flat on the floor.
Raise one knee towards your chest as high as you can, then lower it and repeat with the other leg.
Alternate your legs for one to three minutes while maintaining proper posture.
This exercise stimulates the heart and improves coordination.
While seated, extend your arms to the sides at shoulder height.
Move your arms in small circles, gradually increasing the circle size over 30 seconds, then reverse direction for another 30 seconds.
This movement enhances shoulder mobility and promotes blood circulation.
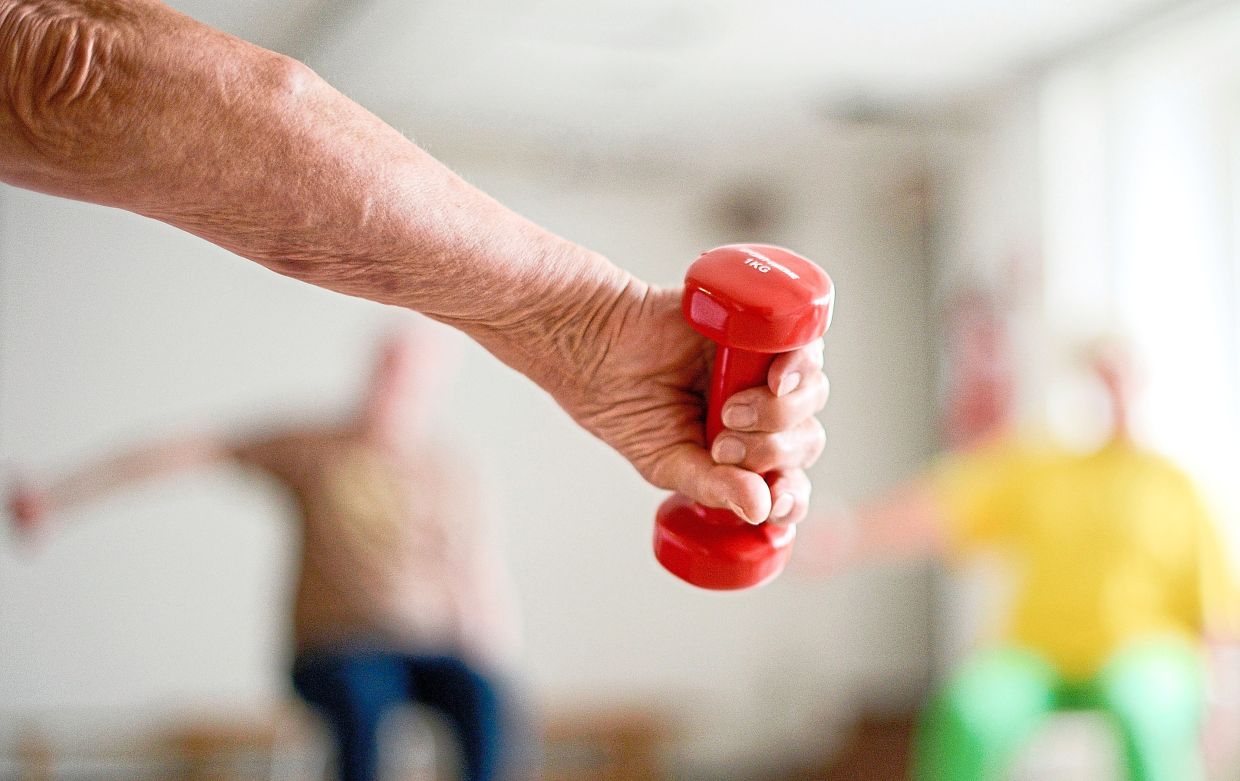
For added intensity, consider holding light weights.
Extend one leg straight out, keeping it parallel to the ground for a few seconds before lowering it.
Repeat 10-15 times before doing the same with your other leg.
To raise your heart rate, combine leg lifts with seated marching or perform the lifts more quickly.
This exercise benefits heart health while also strengthening your legs and improving overall mobility.
Each exercise is designed to be low-impact, yet effective, making them accessible for seniors at all fitness levels.
Exercises for muscle strength
As individuals age, preserving muscle strength becomes increasingly vital for overall health and mobility.
Chair exercises provide a safe and effective means for seniors to build and maintain muscle strength without requiring extensive equipment or risking falls.
Below are some beneficial chair exercises specifically designed to enhance muscle strength in various body areas:
Sit upright in a sturdy chair with your feet flat on the ground.
Slowly extend one leg straight out in front of you, keeping your knee straight and your foot flexed (i.e. in its normal bent position).
Hold the extended position for a count of three before gently lowering your leg back to the starting position.
Repeat this movement 10-15 times before switching to your other leg.
This exercise is an excellent way to strengthen the quadriceps, which are the large muscles located at the front of the thighs.
It also enhances knee stability, which is essential for maintaining mobility.
Sit comfortably in a chair with a weight (such as a dumbbell or a filled water bottle) in each hand, arms resting at your sides.
Keeping your elbows close to your body, lift the weights up towards your shoulders while exhaling.
Pause briefly at the peak of the movement, then slowly lower the weights back to the starting position while inhaling.
Aim for 10-15 repetitions, ensuring proper posture throughout the exercise.
This straightforward, yet effective exercise not only strengthens the arms, especially the biceps, but also enhances grip strength, which can assist in daily activities.
Begin by sitting on the edge of the chair with your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
Slightly lean forward and engage your core.
Gradually rise from the chair by pushing through your heels and standing up, keeping your back straight.
Once fully standing, gently lower yourself back down to the chair, controlling your descent to avoid plopping down.
Repeat this movement eight to 12 times.
Chair squats not only build lower body strength, targeting the glutes, hamstrings and quadriceps, but also improve balance and stability, facilitating everyday activities.
Safety tips
Participating in chair exercises can be an excellent way for seniors to maintain their physical health and well-being, but safety should always be a priority.
Here are some essential safety tips to ensure a safe and effective workout:
Select a sturdy, armless chair with a stable base.
Ensure that the seat height allows your feet to rest flat on the floor.
Keep the area free of obstacles and exercise in a well-lit environment.
Begin with gentle neck rolls, shoulder shrugs and wrist circles as warm-up exercises to prevent injury.
Cool down with seated stretches for your arms, legs and back to maintain flexibility and reduce soreness.
Pay attention to any discomfort during exercises.
If something feels wrong, stop immediately.
If you feel better, then restart gradually.
You can increase the intensity of the exercises as you build strength.
By adhering to these safety tips, seniors can safely enjoy chair exercises while minimising the risk of injury, fostering a sustainable fitness routine and promoting overall health.
Be consistent
As discussed throughout this column, chair exercises offer a valuable opportunity for seniors to maintain their health and well-being, particularly for those who may encounter mobility challenges.
These simple, yet effective routines allow for physical activity without the necessity for extensive walking or standing.
Consistency is key, and even a few minutes each day can lead to significant health improvements.
The benefits of chair exercises also extend beyond the physical realm, contributing to emotional and mental well-being.
We encourage seniors and their caregivers to incorporate these exercises into their regular routines.
By making these movements a part of daily life, seniors can continue to lead active lifestyles, fostering independence and enhancing their quality of life.
By Datuk Dr Nor Ashikin Mokhtar - is a consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist, and a functional medicine practitioner. For further information, email starhealth@thestar.com.my. The information provided is for educational and communication purposes only, and it should not be construed as personal medical advice. Information published in this article is not intended to replace, supplant or augment a consultation with a health professional regarding the reader’s own medical care. The Star does not give any warranty on accuracy, completeness, functionality, usefulness or other assurances as to the content appearing in this column. The Star disclaims all responsibility for any losses, damage to property or personal injury suffered directly or indirectly from reliance on such information.
Related posts: