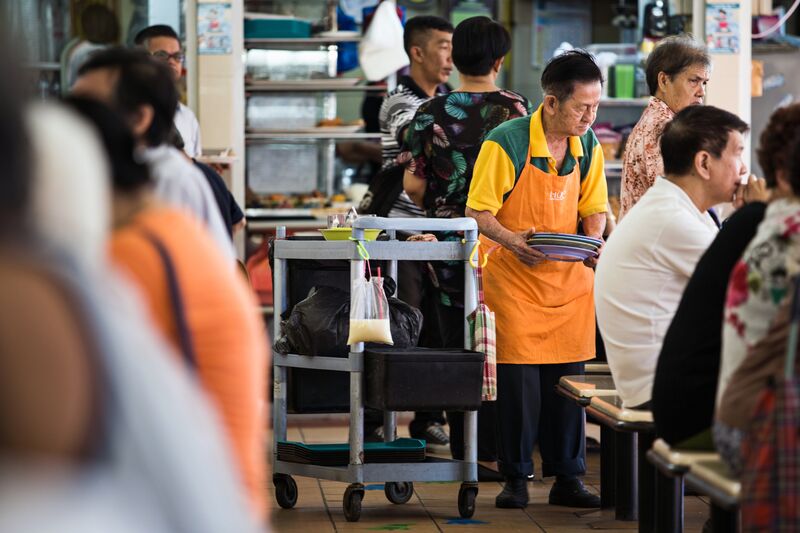
Enough time: Ruslan says there should be adequate time for corporates to implement the guidelines by June 1, 2020.
Will the much-anticipated enforcement of Section 17A of the MACC in less than a year result in a corruption-free business scene?
THE Pakatan Harapan government envisions a corruption-free Malaysia in five years’ time, but the journey towards the ambitious objective will be a bumpy one – especially for Corporate Malaysia.
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers’ Global Economic Crime Survey 2018, about 35% of the Malaysian companies surveyed have suffered as a result of bribery and corruption in their daily operations. This marks a sharp increase from just 19% in 2014.
Speaking with StarBizWeek, Transparency International Malaysia (TIM) president Muhammad Mohan cautions that “corruption is rampant and has worsened in the Malaysian business sector over the last few years”.
Despite the worrying trend in Corporate Malaysia, preventive anti-corruption measures among local companies remain limited.
As at end-May 2019, only 59% of listed companies in the country had an internal anti-corruption policy, according to the Securities Commission (SC).
The good news is, the Pakatan administration has been ramping up its anti-corruption initiatives over the last one year.
About a month after the 14th general election (GE14), the government established the Governance, Integrity and AntiCorruption Centre (GIACC) to monitor and coordinate all activities related to combating graft, integrity and governance.
In January 2019, the National AntiCorruption Plan 2019-2023, which was developed by GIACC, was launched by Prime Minister Tun Dr Mahathir Mohamad. The five-year plan has outlined six priority areas and 115 initiatives to achieve zero-tolerance to corruption and bolster good governance.
On July 18, the SC presented its anti-corruption action plan to the Cabinet Special Committee on Anti-Corruption chaired by Dr Mahathir, with recommendations to prevent corruption, misconduct and fraud.
Section 17A comes into force
In addition to these efforts, beginning June 1, 2020, Corporate Malaysia will take its next step towards a corruption-free business environment via the enforcement of Section 17A of the MACC Act.
The new provision, which was inserted into the anti-bribery act before the GE14, establishes the principle of corporate liability among businesses. Under Section 17A, companies and their directors could be deemed personally liable if an associated person such as an employee or subcontractor is caught involved in corruption for the benefit of the commercial organisations.
Section 17A covers companies, partnerships and limited liability partnerships operating in Malaysia.
The companies and directors could defend themselves against prosecution if they have implemented “adequate procedures” such as internal guidelines or staff training within the commercial organisations.
However, senior lawyer and former Malaysian Bar president Datuk Lim Chee Wee says the existence of adequate procedures does not preclude a commercial organisation or the directors from being charged or prosecuted.
“That is to say, a company may still be charged or prosecuted for corruption offence under section 17A (1), but the fact that the company has in place adequate anti-corruption procedures may absolve it from any finding of criminal liability by the court,” he says.
“However, Section 17A does not put an undue amount of responsibilities on the management. While the definition of associated person under section 17A (6) appears to be general and extensive, there is a safeguard in section 17A (7) which provides for the need for a holistic assessment of the relationship between the company and the associated person to be conducted before any liability of the associated person can be imputed on the company,” he says.
With the anti-bribery provision, companies can no longer hide behind third parties such as consultants or subsidiaries. In the past, holding companies and the board of directors could absolve themselves of any blame if there were corrupt practices at the subsidiary levels.
“Now, the directors and companies are accountable for everything. Even consultants who act for companies come under the MACC Act and the employee hiring processes must be accounted for,” says a CEO of a listed firm.
He adds that the focus should be more on the wide implications of Section 17A, rather than the cost of compliance.
“It is not whether the corporate liability provision is difficult or adds to costs of Malaysian companies.
It is a question of whether the companies and directors are aware of the wide implications with the act coming into force next year.
“The MACC act together with the beneficial ownership laws gives MACC the bite to act on corporations, directors and owners. If they want to get you, they can,” he says.
If found guilty of an act of corruption under the soon-to-be-enforced
Section 17A, the penalties imposed on a commercial organisation would be
severe.
A company could be fined not less than 10 times the value of the gratification or RM1mil, whichever is higher, or be subject to imprisonment not exceeding 20 years, or to both.
In short, it will not be “business as usual” for Corporate Malaysia come 2020.
Delay in compliance
While there are only 10 more months before Section 17A is enforced, many businesses in the country have yet to introduce adequate procedures to prevent corruption in their organisations, in line with the “Guidelines on Adequate Procedures”.
On Dec 10, 2018, Dr Mahathir launched the “Guidelines on Adequate Procedures”, which serve as reference points for any anti-corruption policies and controls an organisation may choose to implement towards the goal of having adequate procedures as required under Section 17A.
SC says that even among the listed companies that have an anti-corruption policy, “the majority of these policies contain gaps when compared to the Guidelines on Adequate Procedures”.
TI-M’s Muhammad Mohan hinted that not all government-linked companies (GLCs) will be ready by June 2020 for Section 17A.
“GLCs especially the larger ones are making preparations to handle the corruption risks involved. The problem is many GLCs and non-GLCs have wasted so much time by not implementing or preparing their organisations for this.
“Many businesses are expecting U-turns or extensions to be given,” he says.
Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers president Datuk Soh Thian Lai says the organisation supports the introduction of Section 17A and has undertaken several sessions to educate its members on the implementation of “adequate procedures” as well as the ISO 37001 Anti Bribery Management System.
As the deadline for the enforcement of Section 17A nears, Soh points out that concerns
remain on the readiness and capacity of the small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in ensuring that adequate internal measures have been put in place to potential acts of corruption. specially still lack the know-how lementing such measures. There e greater capacity building in place to assist SMEs,” he says.
However, among major corporations in uch as those related to Nasional and the Employees Fund, the guidelines are being owed, says a CEO of a listed company.
The compliance department has grown bigger, he says. In an email interview with StarBizWeek, SC says that it will take steps to mandate companies to establish and implement anti-corruption measures.
"While there may be additional costs in putting these anti-corruption in place, it is important for comealise that these measures will m to avail themselves of the statutory ddefence provided for under Section 17A (4) of the MACC Act,” says the commission.
Vulnerable businesses
Past experiences indicate that compaed with procurement, governracts and the construction sector ulnerable to corruption and kickbacks.
While government and key industry ve introduced several anti-coreasures such as open tender corrupt practices continue to be prevalent in such sectors.
In fact, between 2013 and 2018, nearly 43% of the total complaints received by MACC were on the procurement sector.
Experts say that the trend is expected to change as businesses in Malaysia fully comply with Section 17A, following its enforcement. The adoption of anti-bribery ISO 37001 standards will also bolster Corporate Malaysia zero-tolerance approach towards corruption.
Facilities management service provider GFM Services Bhd, which is actively involved in government contracts, welcomes the enforcement of Section 17A.
Group managing director Ruslan Nordin believes the corporate liability provision not only upholds a business’ integrity, but also protects shareholders’ value and preserves profitability of the company.
“We view that there is adequate time for corporates in Malaysia to implement the guidelines by June 1 next year,” he says.
Senior lawyer Lim says that Section 17A imposes a duty on all businesses, its directors and officers to be honest in their internal and external dealings.
“This is to be welcomed, corruption increases the cost of transaction, and with this new provision, it should reduce the cost of business,” he says. UHY Malaysia managing director Steven Chong Hou Nian believes that compliance with Section 17A offers businesses an opportunity to exhibit positive values in their corporate culture.
“I opine that the qualitative gains from Section 17A compliance outweigh the additional costs,” he says.
He was also asked whether Section 17A will be successful in reducing corruption within procurement and tendering for government contracts.
To this, he said that the government has pledged to re-design the entire public procurement system while introduce relevant technologies to facilitate a clean, efficient and transparent procurement regime.
“The effectiveness of what Section 17A seeks to achieve, would naturally be premised upon the ecosystem that the MACC Act would operate within.
“The eventual success of the initiative is anyone’s guess, yet I applaud the nation for boldly taking this step forward. This is indeed a success in its own right,” says Chong.




A company could be fined not less than 10 times the value of the gratification or RM1mil, whichever is higher, or be subject to imprisonment not exceeding 20 years, or to both.
In short, it will not be “business as usual” for Corporate Malaysia come 2020.
Delay in compliance
While there are only 10 more months before Section 17A is enforced, many businesses in the country have yet to introduce adequate procedures to prevent corruption in their organisations, in line with the “Guidelines on Adequate Procedures”.
On Dec 10, 2018, Dr Mahathir launched the “Guidelines on Adequate Procedures”, which serve as reference points for any anti-corruption policies and controls an organisation may choose to implement towards the goal of having adequate procedures as required under Section 17A.
SC says that even among the listed companies that have an anti-corruption policy, “the majority of these policies contain gaps when compared to the Guidelines on Adequate Procedures”.
TI-M’s Muhammad Mohan hinted that not all government-linked companies (GLCs) will be ready by June 2020 for Section 17A.
“GLCs especially the larger ones are making preparations to handle the corruption risks involved. The problem is many GLCs and non-GLCs have wasted so much time by not implementing or preparing their organisations for this.
“Many businesses are expecting U-turns or extensions to be given,” he says.
Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers president Datuk Soh Thian Lai says the organisation supports the introduction of Section 17A and has undertaken several sessions to educate its members on the implementation of “adequate procedures” as well as the ISO 37001 Anti Bribery Management System.
As the deadline for the enforcement of Section 17A nears, Soh points out that concerns
remain on the readiness and capacity of the small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in ensuring that adequate internal measures have been put in place to potential acts of corruption. specially still lack the know-how lementing such measures. There e greater capacity building in place to assist SMEs,” he says.
However, among major corporations in uch as those related to Nasional and the Employees Fund, the guidelines are being owed, says a CEO of a listed company.
The compliance department has grown bigger, he says. In an email interview with StarBizWeek, SC says that it will take steps to mandate companies to establish and implement anti-corruption measures.
"While there may be additional costs in putting these anti-corruption in place, it is important for comealise that these measures will m to avail themselves of the statutory ddefence provided for under Section 17A (4) of the MACC Act,” says the commission.
Vulnerable businesses
Past experiences indicate that compaed with procurement, governracts and the construction sector ulnerable to corruption and kickbacks.
While government and key industry ve introduced several anti-coreasures such as open tender corrupt practices continue to be prevalent in such sectors.
In fact, between 2013 and 2018, nearly 43% of the total complaints received by MACC were on the procurement sector.
Experts say that the trend is expected to change as businesses in Malaysia fully comply with Section 17A, following its enforcement. The adoption of anti-bribery ISO 37001 standards will also bolster Corporate Malaysia zero-tolerance approach towards corruption.
Facilities management service provider GFM Services Bhd, which is actively involved in government contracts, welcomes the enforcement of Section 17A.
Group managing director Ruslan Nordin believes the corporate liability provision not only upholds a business’ integrity, but also protects shareholders’ value and preserves profitability of the company.
“We view that there is adequate time for corporates in Malaysia to implement the guidelines by June 1 next year,” he says.
Senior lawyer Lim says that Section 17A imposes a duty on all businesses, its directors and officers to be honest in their internal and external dealings.
“This is to be welcomed, corruption increases the cost of transaction, and with this new provision, it should reduce the cost of business,” he says. UHY Malaysia managing director Steven Chong Hou Nian believes that compliance with Section 17A offers businesses an opportunity to exhibit positive values in their corporate culture.
“I opine that the qualitative gains from Section 17A compliance outweigh the additional costs,” he says.
He was also asked whether Section 17A will be successful in reducing corruption within procurement and tendering for government contracts.
To this, he said that the government has pledged to re-design the entire public procurement system while introduce relevant technologies to facilitate a clean, efficient and transparent procurement regime.
“The effectiveness of what Section 17A seeks to achieve, would naturally be premised upon the ecosystem that the MACC Act would operate within.
“The eventual success of the initiative is anyone’s guess, yet I applaud the nation for boldly taking this step forward. This is indeed a success in its own right,” says Chong.