|
An aerial view shows the newly completed Huoshenshan Hospital. Digital tools helped coordinate its design and construction-Image: REUTERS |
- Taking advantage of emerging technologies, including Big Data and artificial intelligence, has enabled China to respond rapidly to the impacts of COVID-19 and to fight against its spread;
- New hospitals were built in record time and millions of students were able to resume their learning online thanks to the industrial internet;
- From coordinating community volunteers to offer municipal programmes online, digital platforms have helped empower citizens in the fight against the virus.
The outbreak of COVID-19 has brought huge challenges across the globe.
There are contradictions and conflicts, but also an unprecedented spirit within humanity to defeat this scourge. Beyond national borders, countries are working together to combat the coronavirus, utilizing joint prevention and control mechanisms while sharing resources and information.
Have you read?
- How China can take the lead on protecting nature after COVID-19
- Here's why China’s post-COVID-19 stimulus must reject costly coal power
- China is sending medical experts and supplies to help Italy fight coronavirus
In China, people have joined together to contain the virus’ spread. Their achievements have been nothing short of heroic given the exponential rise in confirmed cases, a huge and densely-packed population and the world’s largest human migration simultaneously occurring during the Chinese New Year festivities in January and February.
The involvement of Tencent, a Chinese internet technology company, in promoting the power of digital, is testament to the rise of the industrial internet in the fight against the virus.
While the consumer internet provides services such as social networking and e-commerce to consumers who are self-isolating, its industrial counterpart, focusing primarily on business and industry, has worked to safeguard society’s normal operation, making a profound contribution which we will call the “ACE effect”.
Accelerator: a new speed record
Incorporating technologies, including 5G, artificial intelligence, Big Data and cloud computing, the industrial internet is a new, pan-industry infrastructure. Connecting data, while promoting data sharing and its evolving importance, enables the coordination of the entire industry chain. This has given the Chinese manufacturing industry a dramatic boost, leading to an amazing string of new production records.
An excellent example is the newly built Huoshenshan and Leishenshan Hospitals, which offer 2,600 beds in total.
Containing the virus’ spread required additional facilities to handle the patient load and construction workers took just 10 days and 12 days respectively to build and equip both. Digital tools like BIM (Building Information Modelling), allowed the hospitals’ design institutes to utilize the industrial internet, bringing together hundreds of BIM designers nationwide. The hospitals’ design plans were produced in 24 hours and construction drawings in only 60 hours. Onsite construction was so well-organized that thousands of machines were monitored and coordinated in real-time through an industrial internet platform.
https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=1421909607991805
From 1 January to 7 February, more than 3,000 Chinese companies incorporated the production of medical supplies into their business scopes, dynamically increasing the production scale of masks, protective clothing and disinfectants. The industrial internet has enabled this rapid, cross-sector production. A well-aligned, start-to-finish and modular industry chain allowed companies to rapidly change processes and produce new product types while absorbing large-scale changes to volume, capacity or capability.
Change-maker: the cyber-world becomes the real world
The outbreak increased the digitalization of sectors including medical services, office work and education. In turn, these newly digital products have reshaped people’s perceptions and behaviours. Society has experienced an irreversible leap into digital life.
Following the outbreak, Tencent, Alibaba and vertical online healthcare platforms like DXY began offering the public remote medical services. People consulted with online doctors, conducted self-assessments and decided whether to go to a hospital for further medical checks or remain at home. These simple screening tools reduced non-essential hospital visits and caregiver workloads while mitigating the risks of cross-infection.
Remote technology has enabled hospitals to share their best resources over great distances. Thanks to China’s 5G networks, many Wuhan hospitals, have been able to connect with counterparts in Beijing, allowing experts in the capital to provide real-time consultation based on ultra-high-definition images.

Keeping 276 million students learning online has advanced the digitalization of education. In mid-February, the government ordered more than a quarter of a billion full-time students to resume their studies through online platforms - the largest “online movement” in the history of education. Hundreds of industrial internet-based online educational platforms now provide free-of-charge, individual live streaming services or share their open class content. During the Spring Festival period, Tencent Classroom alone added nearly 1.28 million new users.
Starting with remote offices, the digitalization of business and human resource management has moved up the agendas of corporate managers. Online collaborative platforms from Tencent, Alibaba, Huawei, Byte Dance and Baidu have been refined to meet surging consumer demand. Tencent Conference added more than 100,000 Cloud Hosts in only eight days between 29 January and 6 February.
Enabler: a new co-governance model for modern society
During this period a new type of social governance has arisen; one enabled by the industrial internet. Governments now actively engage partners to improve the efficiency and quality of municipal services. Empowered by digital tools, communities and people are active stakeholders in social governance. Co-governance, involving multiple participants, is emerging as a new model for today’s increasingly complicated society.
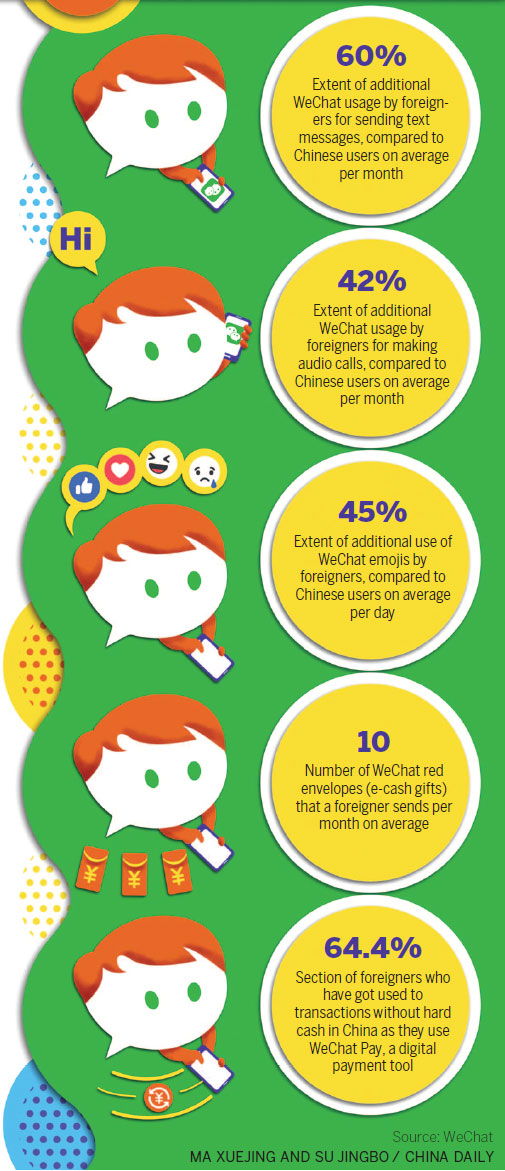
In China, the digital provision of municipal services infiltrates government agencies in many cities. The outbreak has expedited this process and agencies have digitized further. By 8 February, there were 100-plus municipal service “mini programmes” featuring epidemic status information. On WeChat, these programmes grew their users by nearly 60% in under 3 weeks.
Importantly, the industrial internet has empowered communities and people in the war against COVID-19. Through digital platforms, volunteer teams of residents within communities assist in disinfection and deliver supplies aided by digital community management and communication tools.

US cases of COVID-19 have now surpassed those in China US cases of COVID-19 have now surpassed those in China Image: Statista
In addition, the advent of the “Health QR Code” lets users submit information regarding travel to major epidemic outbreak regions and details close contact with infected people and other relevant information. A three-colour scale indicates the person’s recent virus-related health history, enabling them to cooperatively comply with virus-related prevention and control policies.
Through the “ACE effect”, the industrial internet provides a fundamental infrastructure for empowering individuals and organizations. Enterprises, government and individuals have all actively engaged in the war on COVID-19 through the advantage supplied by this technology and the advantage this creates has helped China to almost stop the outbreak.
What is the World Economic Forum doing about the coronavirus outbreak?
A new strain of Coronavirus, COVID 19, is spreading around the world, causing deaths and major disruption to the global economy.
Responding to this crisis requires global cooperation among governments, international organizations and the business community, which is at the centre of the World Economic Forum’s mission as the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.

The Forum has created the COVID Action Platform, a global platform to convene the business community for collective action, protect people’s livelihoods and facilitate business continuity, and mobilize support for the COVID-19 response. The platform is created with the support of the World Health Organization and is open to all businesses and industry groups, as well as other stakeholders, aiming to integrate and inform joint action.
As an organization, the Forum has a track record of supporting efforts to contain epidemics. In 2017, at our Annual Meeting, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) was launched – bringing together experts from government, business, health, academia and civil society to accelerate the development of vaccines. CEPI is currently supporting the race to develop a vaccine against this strand of the coronavirus.
The Forum has created the COVID Action Platform, a global platform to convene the business community for collective action, protect people’s livelihoods and facilitate business continuity, and mobilize support for the COVID-19 response. The platform is created with the support of the World Health Organization and is open to all businesses and industry groups, as well as other stakeholders, aiming to integrate and inform joint action.
As an organization, the Forum has a track record of supporting efforts to contain epidemics. In 2017, at our Annual Meeting, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) was launched – bringing together experts from government, business, health, academia and civil society to accelerate the development of vaccines. CEPI is currently supporting the race to develop a vaccine against this strand of the coronavirus.
These enabling capabilities will outlast the COVID-19 pandemic and make lasting contributions to the sustainable development of mankind. Tencent’s partnership with the UN, in recognition of its upcoming 75th anniversary, is a good example. The initiative will ask millions of participants worldwide how our planet should look in 2045 and what role international cooperation can play in solving our common challenges, both now and in the future.
For most people alive today, anywhere in the world, we have never faced a crisis of such magnitude. It is the first true test of our ability to stand together in the face of a common enemy.
Now is the time for neighbourliness, not hostility. Let this event serve as a wake-up call: our governments must be responsible to the people and enter into a collaborative relationship for the well-being of this and future generations. Should we lose, then we lose together; when we achieve victory it will be because we did it together.
Lau Sengyee, Senior Executive Vice President, Chairman of Group Marketing and Global Branding, Tencent
Source link
Read more:
Tech vs pandemic: Govt bodies and companies turn to apps and AI to combat the Covid-19
 Can China's exports survive pandemic after surviving domestic outbreak?
Can China's exports survive pandemic after surviving domestic outbreak?
After Wuhan, capital city of Central China's Hubei Province hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic in the country, lifted its city lockdown after 76 days in isolation to contain the novel coronavirus spread, China officially entered the next stage of combating the virus.
China's miracles beyond biased Western understanding
It is time for the US to accept the fact: China is indeed working miracles, and will certainly do more. Realizing this reality will benefit the US itself and China-US relations.Related Posts:
https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2020/04/07/rm10bil-a-boon-for-smes-and-workers?jwsource=cl https://youtu.be/wGzVdeA3b0g ...
Beijing is helping the US and other unfriendly countries to combat the Covid-19 pandemic, but is this kind gesture worth it? https://y..
Tech Titans of China
Unknown Chinese startup creates the world's most valuable Bytedance
今天,中美正式摊牌!百年国运之战已经开始!
https://youtu.be/KKJ6em7g53o